Leverage customer data to personalize experiences and boost sales! This article explores customer data management (CDM) best practices, covering data collection, security, compliance, and tools like CRMs, DMPs, and CDPs.
The Gist
- Personalization impact. Effective customer data management (CDM) allows businesses to offer the personalized experiences consumers crave.
- Data security priority. Prioritizing data security within CDM practices protects consumer information, builds trust, and helps compliance with regulatory standards.
- Tool selection insight. Choosing the right customer data management tools, such as CRMs, DMPs, CDPs, and BI, is crucial for streamlining data tracking and driving strategic decision-making.
The more businesses understand their customers — where they live, what they like or dislike, what influences their purchasing decisions, etc. — the easier it is to provide a good customer experience.
One Statista survey revealed that 56% of consumers expect marketing offers to always be personalized, and 73% said companies should understand their unique needs and expectations.
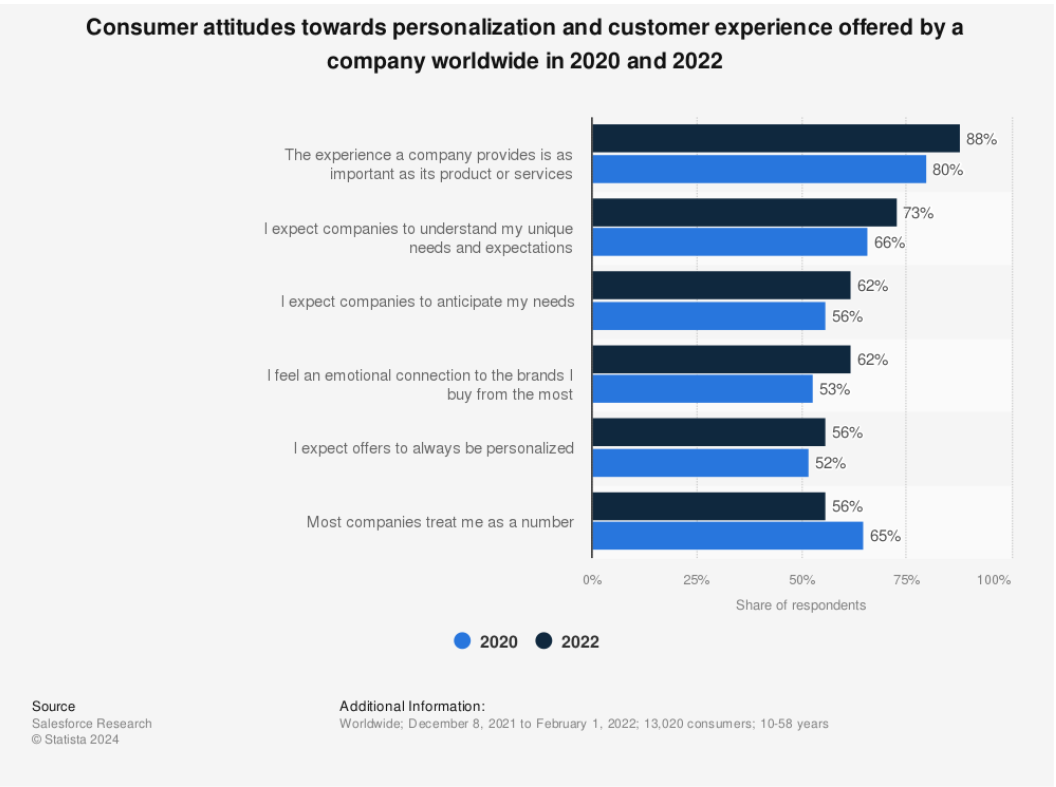
How can brands tap into that personalization? It all comes down to data. Handling that data appropriately, including not alienating customers by asking for excessive information or, worse, losing that data, means companies must practice good customer data management (CDM).
What Is Customer Data Management?
Customer data management (CDM) centralizes customer information to improve decision-making and personalize experiences. It involves collecting, analyzing and securely storing data from various touchpoints, allowing businesses to understand consumer behaviors and preferences. Effective CDM practices help improve customer satisfaction and offer a competitive advantage in a data-driven market.
3 Types of Customer Data
When creating a customer data management plan, you must understand the different types of data you collect. Once you do, you can decide which data categories fulfill your business functions and improve the customer journey.
Data falls into three types:
1. Identity Data
Most websites collect this relatively basic information when customers purchase, download an asset (such as an ebook or white paper), or subscribe to email updates.
Identity data includes the customer’s:
- Name
- Date of birth
- Gender (with “Prefer not to say” or “Undefined” options)
- Phone number and phone type (landline or mobile)
- Email address
- Home address (including city, state, zip code, and country)
2. Attribute Data
Attribute data tells you a bit more about each customer. Companies or organizations can collect attribute data using surveys, phone interviews, or interactions in a chat box. This data helps you create a complete picture of your customer as you move toward an ideal customer profile.
Attribute data includes the customer’s:
- Job title (including boxes for retired or self-employed)
- Income level (asking for ranges is better than asking for specifics)
- Marital status
- Number of children
- Vehicle (including make, model, and year)
3. Behavioral Data
Behavioral data offers clues on how potential or current customers interact with your company, including online and in-store.
Behavioral data includes:
- How many times a person visited your website
- How long do they stay on a page
- How many emails did they open and read
- If they place items in a shopping cart but leave the website before purchasing
- What goods or services do they buy, how often, and what price they pay
- If they return products and how often
- If they shop in-store and how often compared to online visits
- If they use a rewards or loyalty card when shopping in-store
All of this data helps you create the ideal customer profile. It will help you focus your marketing efforts and speak directly to the kind of customer for whom your product or service solves a problem.
Also Read: CRM vs. CDP – Understanding the Key Differences
9 Principles to Improve Your Customer Data Management
Any business that wants to improve data collection even slightly needs to learn how to manage customer data appropriately. Observing the following principles can help your business get the most out of your data collection efforts while ensuring your customers continue to enjoy a positive experience.
1. A Data Governance Strategy
Data governance helps identify the data you need and how you will collect it. It’s also a playbook for all employees on how to collect data, where to store it, and how to secure it.
Data governance involves standardizing data collection across your business. It ensures that you collect all data according to your company’s principles and relevant legal regulations. Plus, any changes you make to data collection must go through the correct channels.
2. Targeted Data Collection
Just because you can collect certain data points doesn’t mean you should. If you do, you might encounter a data deluge — so much information that you don’t know what to do with it all.
Be specific. Proper client data management means only collecting the data you need to help your company. You should audit and check every piece of information you collect. Ask yourself:
- Who needs this data?
- How does this data help build our company and improve customer experience?
- If we don’t collect this data, would it hinder our operations?
3. Avoiding Data Siloes
Silos may work well on a farm, but a data silo can be a problem. You don’t want every department in your company to collect data and then not share it — or, worse, duplicate their efforts by collecting the same data.
Sharing data improves customers’ experiences with your brand. When the departments in your company collaborate on customer data management, you achieve a 360° picture of the customer journey. Nothing is more frustrating for a customer than speaking with a representative and being asked questions they already answered during another interaction. Data collaboration eliminates these frustration points.
4. A Focus on Data Security
According to a CB Insights report, cyber attacks more than doubled in 2023. The global average weekly cyberattacks per organization hit an all-time high of 1,258 in the second quarter of 2023. The average data breach cost has also grown 15% in the last three years. While the average data breach costs companies $4.5 million, the largest threats drive more than $100 million losses.

Securing data must be one of your business’s top priorities. Not only can overlooking this step cost your organization time and money, but it can also erode consumer trust.
5. The Right CDM Platform
Whatever customer data management system you select, ensure it meets all up-to-date security standards and laws. Watch for changes to the platform you’re using or potential risks that might arise. You must also constantly review and improve your security policies.
6. A Data Accuracy Process
Let’s say one of your departments collects information on the date of purchases using the MM/DD/YY format. However, another department collects similar data using the DD/MM/YY format. This setup can result in a lot of confusion and useless data.
Marketing data management includes going through your data stores and eliminating this bad data — information that’s inaccurate, outdated, redundant, or improperly formatted.
To avoid bad data going forward, your data collection efforts should involve as few humans as possible. The more human hands that touch data collection, the more likely you’ll find mistakes and inaccuracies. Using automatic data validation tools helps eliminate this problem. Another idea is to perform a data audit regularly. Cleaning out old, no longer valuable data leads to fewer mistakes and happier customers.
7. Compliance With Data Regulations
Customers care about data privacy. While they may not mind you collecting data if it ensures better experiences, they still want you to ask for permission. They may also be willing to share some data points but still want to maintain privacy in other areas.
You need to ask customers what data you can gather from them. In some cases, you’re legally required to do so. For instance, you might have to conform to data laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). You should also inform customers what your data collection processes look like. Transparency here is the key to winning customer trust.
Think about what happened when Facebook allowed Cambridge Analytica to collect user data without telling people what they were doing. When it became public, it created many financial problems for Facebook and legal issues for Cambridge Analytica.
8. Multiple Data Backups
Unintentionally losing data can be difficult. However, the day may come when a power outage, natural disaster, or employee mistake will result in a significant loss of information. In fact, according to Netwrix, human error is the number one reason for data loss, followed by phishing attacks and poor password policies.
Every business and organization, regardless of size, should have a data backup and recovery plan in place as part of their customer database management.
9. Ongoing Team Training
Why bother creating a user data management plan if your employees don’t know how to implement it? Seek feedback from your employees about ideas for your CDM plan. The employees on the front lines of data collection will likely have useful suggestions for protecting, sharing, and using it.
Regardless, every member of your team who handles data management or data collection needs to know and understand your company’s data governance strategy. That includes all areas, such as data collection, marketing, legal, and IT.
What Are the Benefits of Customer Data Management?
Customer data management provides businesses with a multitude of benefits, including:
- A unified view of customer interactions across all channels
- Enhanced data accuracy and accessibility
- Improved data security
- Increased opportunities to upsell and cross-sell
- Increased customer retention and loyalty
- Higher customer acquisition rates
- Increased campaign effectiveness and return on investment (ROI)
- Greater customer satisfaction and trust
What Tools Are There for Customer Data Management?
A number of customer data management solutions are available, with each designed to cater to different aspects of the data management process.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
Customer relationship management systems streamline the tracking and management of all customer interactions and data. CRMs help businesses build a comprehensive customer information database, including contact details, purchase history, preferences, and interactions across all touchpoints.
A CRM can enable sales, marketing, and customer service teams to access real-time, actionable insights, fostering personalized customer experiences and improving relationship management.
Data Management Platforms (DMPs)
Data management platforms focus on collecting, organizing, and analyzing large volumes of data from diverse sources, including first-party data, third-party data, and online interactions.
DMPs are particularly valuable in digital marketing. They allow advertisers to segment audiences, tailor messaging, and optimize advertising campaigns across various channels. Although not exclusively for customer data, DMPs play a vital role in understanding broader market trends and customer segments.
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs)
Customer data platforms are a more specialized and comprehensive customer data management solution. They integrate data from multiple sources to create a unified, persistent customer database that is accessible to other systems.
CDPs collect data across all customer touchpoints, providing a 360-degree view of the customer journey. Unlike CRMs and DMPs, CDPs focus on aggregating and unifying complex data sets to provide a single customer view.
Marketing Automation Platforms
These tools automate repetitive marketing tasks, such as email marketing, social media posts, and ad campaigns. By leveraging marketing automation, businesses can ensure they not only collect and manage customer data effectively but also use this data to engage customers with personalized marketing messages at scale.
Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
Business intelligence solutions are essential for analyzing complex data sets and transforming them into actionable insights. BI tools aggregate data from various sources, including customer data platforms, to perform in-depth analysis, reporting, and data visualization.
While not exclusively focused on customer data, these tools are important for leveraging that data to inform broader business strategies.
Also Read: AI Will Breathe New Life Into Market Research
Support Customer Data Management With Positive Practices
Clean, accurate data backed by a management plan can help you attract new prospects, create a better experience for your current customers, and improve your bottom line. The more attention you pay to customer data management, the more ways you can use collected data positively.










